water treatment Plant
Water Supply Mega Project (Phase I) – Transforming Faisalabad’s Water Supply Infrastructure
Access to clean and reliable drinking water is a fundamental right, yet it remains a challenge for many growing cities. The Water Supply Mega Project (Phase I) in Faisalabad has proven to be a landmark initiative addressing these issues, ensuring the delivery of potable water to its residents. This blog explores the background, objectives, and achievements of this groundbreaking project, which stands as a testament to innovative urban water management.

Background of the Project
Key Highlights:
Scope of the Project
- A 10 MGD Surface Water Treatment Planty 44 MGD in Phase I
- 10 tube wells at Gutwala, contributing 5 MGD to the water supply system.
- Installation of a new arterial main spanning 7.52 km with a 1000 mm diameter.
- A 12.96 km transmission main to facilitate water transport
- Implementation of advanced techniques for network zoning, bulk metering, hydraulic modeling, and leak detection, significantly improving the efficiency of water distribution.
Objectives and Achievements
The primary objective of the project was to augment Faisalabad’s water supply by an additional 15 million gallons per day (MGD), addressing the city’s increasing water demand. Secondary objectives included enhancing the water supply distribution network and reducing non-revenue water (NRW). These goals have been successfully achieved, resulting in:
- Increased access to clean water for the city’s population.
- Improved water network efficiency, ensuring equitable distribution across regions.
- Sustainable management of water resources to meet the growing urban demand.
Impact on the Community
Conclusion
Construction of Distribution Center, Rehabilitation of Old Jhal Khanuana Water Treatment Plant (JICA Grant-in-Aid)
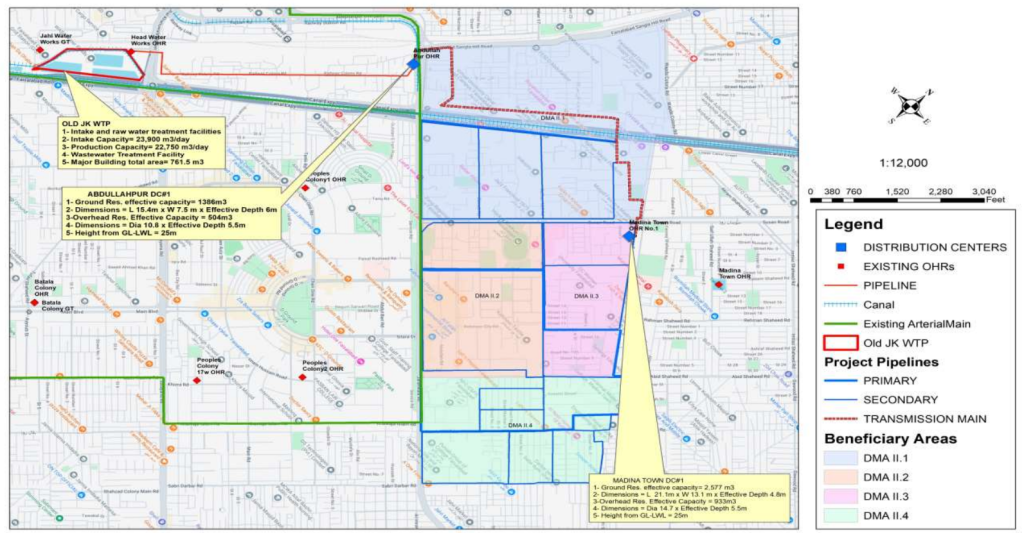
Background of the Project
- SWTP (Sewage Water Treatment Plant) was originally constructed in 1896.
- It was rehabilitated in 1984.
- The current capacity of the plant is 3.5 MGD (Million Gallons per Day).
- As per the Master Plan 2018–2038, it is a priority project to enhance the plant’s capacity to 5 MGD.
Scope of the Project
- Rehabilitation & enhancement of WTP (5 MGD)
- Transmission line (4.1KM)
- Construction of ground reservoirs (GST) (2Nos)
- Construction of overhead reservoirs (OHR) (2Nos)
- Distribution System (primary, secondary & tertiary) network
Project cost
Total PKR 7866.70 million
L.C: PKR 1230.70 Million
F.C: PKR 6636 Million
Expenditure till date
L.C: PKR 1050 Million
F.C: PKR 6616 Million (JPY 3235.35 Million)
Progress
Outcomes
- Enhanced production capacity of the Water Treatment Plant
- Water security through new transmission and distribution system
- 0.2 Million Population will be benefitted
Current Status
- Contract Agreement signed on September 2022 with M/s Tobishima Corporation, Japan.
- Project has been completed within stipulated time period according to the Contract Agreement i.e. March 2025.
- Project is in testing / commissioning stage.
Issue
- Release of funds amounting Rs. 180.00 million is awaited
